-
배열의 응용 - 다항식 표현, 덧셈,컴퓨터 공부/자료구조 2020. 3. 24. 14:09
- 다항식의 형태
p(x)= a_n x^n+a_(n-1) x^(n-1)+ …+a_1 x^1+a_0
- 다항식의 처리
–> 어떻게 저장할 것인가
–> 어떻게 연산을 할 것인가
- 다항식을 저장하는 방법
–> 다항식의 모든 항을 배열에 저장
x^5+6x+3
typedef struct { int degree; //차수 float coef[MAX_DEGREE]; //계수 } polynomial; polynomial a = { 5, {1, 0, 0, 0, 6, 3} };ex) 3x^5+6x+3과 7x^4+5x^2+1 을 더하기
#include <stdio.h> #define MAX(a,b) (((a)>(b))?(a):(b)) //큰 수 반환 #define MAX_DEGREE 101 typedef struct { // 다항식 구조체 타입 선언 int degree; // 다항식의 차수 float coef[MAX_DEGREE];// 다항식의 계수 } polynomial; // C = A+B 여기서 A와 B는 다항식이다. polynomial poly_add1(polynomial A, polynomial B) { polynomial C; // 결과 다항식 int Apos=0, Bpos=0, Cpos=0;// 배열 인덱스 변수 int degree_a=A.degree; //A다항식의 차수 int degree_b=B.degree; //B다항식의 차수 C.degree = MAX(A.degree, B.degree); // 결과 다항식 차수(A,B 중 더 큰 차수) while( Apos<=A.degree && Bpos<=B.degree ){ //둘 중 하나 차수가 끝날 때까지 if( degree_a > degree_b ){ // A항 > B항 C.coef[Cpos++]= A.coef[Apos++]; //A항 계수 그대로 degree_a--; //다음 항으로 } else if( degree_a == degree_b ){ // A항 == B항 C.coef[Cpos++]=A.coef[Apos++]+B.coef[Bpos++]; //A항 계수 + B항 계수 degree_a--; degree_b--; //다음 항으로 } else { // B항 > A항 C.coef[Cpos++]= B.coef[Bpos++]; //B항 계수 그대로 degree_b--;//다음 항으로 } } return C; // 결과 다항식 반환 } int main( ) { polynomial a = { 5, {3, 0, 0, 0, 6, 3} }; //값 넣어주기 polynomial b = { 4, {7, 0, 5, 0, 1} }; polynomial c; c = poly_add1(a, b); }–> 다항식의 0이 아닌 항을 배열에 저장
x^5+6x+3
struct { float coef; //차수 int expon; //계수 } terms[MAX_TERMS]={ {1,5}, {6,1}, {3,0} }; //2차 배열 (차수, 계수)쌍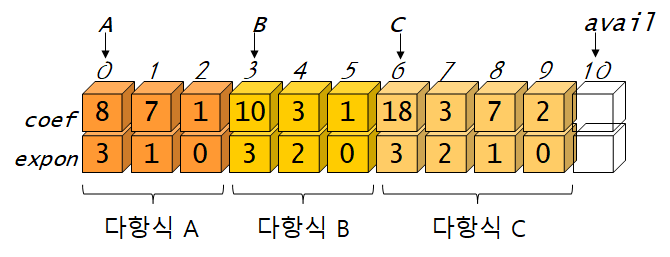
하나의 배열에 3 개의 다항식을 두고 있다 ex) 8x^3+7x+1과 10x^3+3x^2+1 을 더하기
#define MAX_TERMS 101 struct { float coef; int expon; } terms[MAX_TERMS]={ {8,3}, {7,1}, {1,0}, {10,3}, {3,2},{1,0} }; int avail=6; //결과 넣을 배열의 인덱스 시작점 char compare(int a, int b)// 두 개의 정수를 비교 { if( a>b ) return '>'; else if( a==b ) return '='; else return '<'; } void attach(float coef, int expon)// 새로운 항을 다항식에 추가한다. { if( avail>MAX_TERMS ){//배열 공간 가득 fprintf(stderr, "항의 개수가 너무 많음\n"); exit(1); } terms[avail].coef=coef; //넣기 terms[avail++].expon=expon; //인덱스 뒤로 이동 } int main() { int Cs, Ce; //결과 다항식의 시작, 끝 인덱스 poly_add2(0,2, 3,5, &Cs,&Ce);//A다항식의 시작과 끝, B다항식의 시작과 끝, 결과 다항식의 시작, 끝 인덱스 } poly_add2(int As, int Ae, int Bs, int Be, int *Cs, int *Ce) { float tempcoef; *Cs = avail; while( As <= Ae && Bs <= Be ) switch(compare(terms[As].expon,terms[Bs].expon)){ case '>': // A의 차수 > B의 차수 attach(terms[As].coef, terms[As].expon); As++; break; case '=': // A의 차수 == B의 차수 tempcoef = terms[As].coef + terms[Bs].coef; if( tempcoef ) attach(tempcoef,terms[As].expon); As++; Bs++; break; case '<': // A의 차수 < B의 차수 attach(terms[Bs].coef, terms[Bs].expon); Bs++; break; } for(;As<=Ae;As++)// A의 나머지 항들을 이동함 attach(terms[As].coef, terms[As].expon); for(;Bs<=Be;Bs++)// B의 나머지 항들을 이동함 attach(terms[Bs].coef, terms[Bs].expon); *Ce = avail -1; }'컴퓨터 공부 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
스택 응용 (0) 2020.03.24 스택 (0) 2020.03.24 재귀함수 (팩토리얼, 피보타치 수열, 하노이 타워) (0) 2020.03.20 선택 정렬 (0) 2020.03.20 순차 탐색 , 이진 탐색 (0) 2020.03.20